WHAT IS THE SPI RESIN IDENTIFICATION CODE?
In 1988, The Society of the Plastics Industry (SPI), now known as the Plastics Industry Association, created the Resin Identification Code (RIC) system. This system was developed to provide a consistent national program to help sorting line workers identify post-consumer packaging types using the six basic packaging resin classes. Contrary to popular belief, the codes weren't intended to be consumer-facing recycle symbols for plastics. The RIC system was supposed to be used to identify the types of plastic resin used to make common products like bottles and other packaging during the processing stage before recycling.

Meaning Of SPI Codes
Not long after the system was introduced, 39 states mandated that bottles and containers be marked with the recycling plastic codes to assist source segregation at households. The codes are as follows:
|
Code Number and Symbol |
Description |
Common Uses |

|
Polyethylene Terephthalate or PET/PETE This resin is clear, tough and has excellent moisture barrier properties. When it's cleaned and recycled, PET flakes and pellets are in demand for carpet yarn fibers, fiberfill and geo-textiles. |
Beverage bottles, food jars, oven film and microwave food trays, carpet strapping, textiles, engineering moldings |

|
High Density Polyethylene or HDPE This resin is used to make translucent bottles and offers good barrier properties and stiffness. It's good for products that don't have a long shelf life (milk). It's also used for industrial and household chemical packaging because of its chemical resistance. |
Milk jugs, cosmetic packaging, shampoo bottles, detergent bottles, plastic lumber, buckets, flowerpots, fencing |

|
Polyvinyl Chloride or PVC/ Vinyl This resin has stable physical and electrical properties, good chemical resistance and strong weatherability. It has two main classes — rigid and flexible materials. |
Pipes, gutters, floor tiles, mud flaps, traffic cones, garden hoses, carpet backing, loose-leaf binders |

|
Low Density Polyethylene or LDPE Given its toughness, LDPE is used to make film. It's also very tough, flexible and used frequently for heat sealing applications because of its relative transparency. It's also used to make flexible lids and packaging and is good for wire and cable applications. |
Shipping envelopes, garbage can liners, floor tile, furniture, outdoor lumber, film and sheet |

|
Polypropylene or PP PP is strong, has good chemical resistance and a high melting point. It's often used for hot-fill liquids and can be incorporated in flexible and rigid packaging. |
Automotive applications - large molded parts, car battery cases, signal lights, ice scrapers, bike racks and oil funnels. Non-automotive - Garden rakes, storage bins, shipping pallets, trays |

|
Polystyrene or PS PS can be rigid in composition or foamed. It has a low melting point and can be clear, brittle and hard in its general-purpose form. PS has an excellent moisture barrier for products with a short shelf life. It also offers outstanding optical clarity and low thermal conductivity. |
Thermal insulation, light switch plates, foamed foodservice applications, plastic moldings, EPS foam protective packaging |

|
Other This is for resins outside of the six main classifications, or it can mean that a product is made of more than one resin. |
Bottle and plastic lumber applications |
Challenges of the RIC System
The public's' misinterpretation of the codes, particularly OTHER, has become a serious problem. The six basic resin classes (recycling numbers) sometimes aren't sufficient enough to meet the needs of recyclers, particularly with regard to new resins and multi-material construction.
Back in 2008, SPI asked ASTM to take ownership of the codes. ASTM agreed and initiated work to convert the system to the ASTM standard format and address various issues using the ASTM's consensus-based process. The latest revisions were done in 2013. One major change was the redesign of the symbols. The chasing arrows symbol around the resin numbers became a solid equilateral triangle around the number. It's believed that this would help bring the focus back to the system's core mission — to facilitate resin identification and quality control before the recycling stage.
Updated Symbols Chart
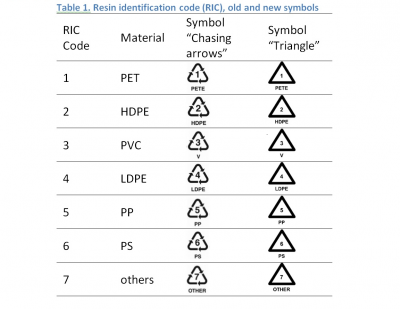
Source: Food Packaging Forum
How Can You Do Your Part?
Even though a lot of these resins are in high demand these days, whether it's in their original or post-use forms, many recycling centers might not be equipped to process them. The good news for you is that their loss is your gain. With the right recycling equipment, specifically EPS, EPP or EPE recycling compactors, you can help ensure that your business is sustainable and more profitable. Foam Equipment and Consulting Co. can help you get your recycling program up and running. Contact us today to learn more about our product offerings and how they can keep you in the green.
Related Articles




